All You Need To Know About America's Opioid Crisis
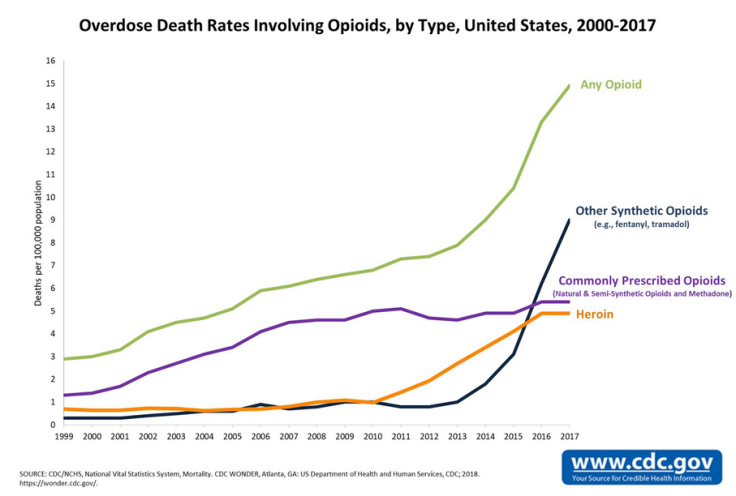
Overdose of opioids, including prescription pain relievers, fentanyl, and heroin, claims 130 lives daily in America, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Opioid overdose cases saw an increase of 30 percent from July 2017 to Sep. 2017 in 45 states. In 2017 alone, nearly 47,000 Americans lost their life after overusing opioids, .
Apart from the loss of life, the opioid crisis has resulted in the social and economic burden on the country. According to the CDC, the “economic burden” of prescription opioid misuse alone in America is $78.5 billion a year. This includes the cost of healthcare, addiction treatment, lost productivity, and criminal justice.
Opioid use by mothers during pregnancy can lead to opioid withdrawal symptoms in newborns, called Neonatal Abstinence Syndrome (NAS). Babies born with NAS have lower birth weight and respiratory problems. From 2004 to 2015, there was a five-fold increase in newborns born with NAS.
Increased use of injectable opioids has also contributed to the spread of HIV and Hepatitis C.
Reasons Behind The Opioid Crisis
Opioid misuse started in the late 1990s when pharmaceutical companies claimed that using opioids for pain management will not become an addiction. Healthcare providers began prescribing opioid pain relievers to patients in large numbers. By scientific observation, it was discovered that prescription pain relievers including synthetic opioid can be highly addictive.
Disturbing Facts about Opioid Use
- 21 to 29 percent of patients who are prescribed opioid pain relievers misuse them.
- 8 to 12 percent of patients misusing opioids get addicted to them4.
- 4 to 6 percent of opioid addicts turn to heroin later.
- Nearly 80 percent of heroin users first misused prescription pain killers3.
- Every 15 minutes, a baby is born suffering from NAS.
- In 2014, State Medicaid had to pay 82% of the total NAS cost treatment which amounted to $563M.
Remedial Measures
To fight the opioid crisis, the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) has adopted a five-pronged approach:
- Spreading awareness about the epidemic by improved health surveillance
- Improving access to treatment facilities
- Promoting the use of overdose-reversing drugs
- Supporting research efforts in alternate pain management treatments
- Promoting better pain management practices
In 2017, the National Institutes of Health (NIH), a division of HHS dedicated to solving the opioid crisis, met pharmaceutical companies to discuss alternate pain management drugs, innovative medication to treat opioid addiction, and safe pain management treatments that can be prescribed without the danger of addiction.
© Copyright IBTimes 2024. All rights reserved.




















