Cheap Oil Is Blocking Progress On Climate Change

The relationship between supply and demand, a fundamental economic concept, holds that when the price of something rises, people use less of it. Similarly, when prices fall, they use more.
And it may seem logical that low oil prices benefit consumers, countries, even the world. When consumers save money on gas, they can spend it elsewhere.
Yet, I argue that climate change makes this view obsolete.
That’s because cheap oil has two big downsides along with its short-term gains. It erodes the advantages of vehicles that get more miles to the gallon, making consumers less apt to do their share to reduce emissions by buying vehicles that use less fuel – or none at all.
It also makes the case for energy innovation seem less urgent to policymakers and the automotive industry.
What’s not to like?
Burning fossil fuels, the main source of manmade carbon dioxide, is the biggest cause of climate change. In the U.S. and other wealthy countries, oil is the single largest source of these emissions.
But relatively low prices are boosting petroleum sales worldwide. Consumption is climbing particularly in Asia, where a sustained economic boom has lifted billions out of poverty and put millions more people behind steering wheels.
Those new middle-class and wealthy consumers and the industries spawned by meteoric economic growth are burning millions of barrels of petroleum every day. This includes transport of goods by road, rail, water and air. But it is passenger vehicles that dominate global mobility, and they are consuming the greatest volume of fuel in the U.S., China and everywhere else.
To be sure, petroleum is the raw material for a great many products besides gasoline, diesel and other fuels – from lipstick to asphalt. The economic benefits of cheap oil can be widely distributed, bolstering growth and keeping inflation down.
President Donald Trump, expressed this view when he likened low oil prices to “a big tax cut for America and the world” in a tweet.
Guzzling more gas
But cheap oil has other effects as well. After improvements in fuel economy during the 1970s and early 80s, two decades of low gasoline prices reversed this trend, causing average miles per gallon to actually decrease a little in some years. Only in 2004, when prices rose, did fuel economy again become an issue.
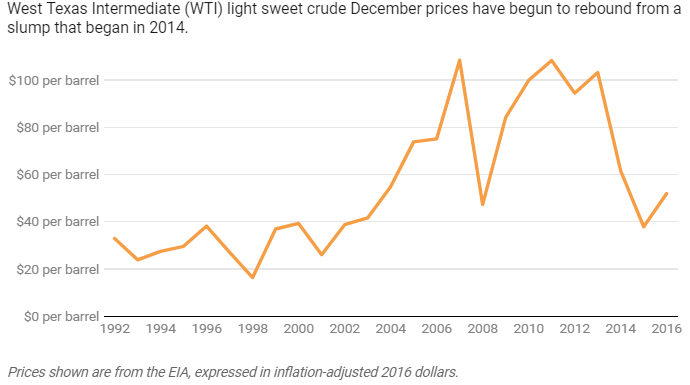
After years of hovering around and even topping US$100 per barrel, aside from a brief peak during the Great Recession, oil prices collapsed. They fell to less than $50 by the end of 2014 and sank even lower in early 2015.
Oil prices are still nowhere near $100 a barrel.
Oil prices since 1992
Americans responded as economists would expect them to: by driving more. The lower prices fell, the less it cost to fill their tanks. Summertime gas consumption hit an all-time high.
Unsurprisingly, U.S. emissions from transportation rose by 10 percent between 2014 and 2017, even as they fell for electricity generation and other sectors.
In addition, drivers bought bigger vehicles. Sales of SUVs, minivans and small pickups soared, while passenger car sales plummeted.
By 2018, Americans were buying two SUVs or pickups for every sedan. The trend, also present in Europe, is a core reason why emissions have risen from advanced nations for the first time in five years.
Automakers are responding by phasing out passenger car production and manufacturing more SUVs and trucks in a trend that reaches beyond U.S. borders. SUV sales are surging around the world.
Partly due to the extra miles driven and the size of the vehicles involved, carbon dioxide emissions from wealthy nations rose by 0.5 percent in 2018, following five years of decline.
No one calls the shots
But who controls oil prices? As an energy scholar and former petroleum geoscientist, I believe that it’s clear that no one does.
Governments can establish climate policies, such as carbon pricing, stiff fuel taxes and other measures, that raise gasoline prices. But, as the recent French protests and two defeats in a row in Washington state for a carbon fee or tax have shown, there are limits to how far or fast they can go, even in rich countries.
And low-income nations view such measures as damaging and intrusive. Raising fuel prices has inspired massive resistance, even riots, in nations as diverse as India, Iran, Mexico and Haiti.
The Organization of Petroleum Exporting Countries has teamed up with Russia to create an oil-exporting alliance known as OPEC+. Those countries can cut supplies to increase prices, as they agreed to do in December 2018. They can also increase output, should they wish to lower prices.
Yet that doesn’t mean that exporters have the power to call all the shots. For example, if China – the world’s largest oil importer – were to have a big recession, Saudi Arabia and Russia would probably have trouble finding buyers for all of the oil they want to export. Overproduction in that scenario would make oil prices sink.
There is another reason the group can’t dominate. They must compete against the world’s largest oil producer and most rapidly growing crude exporter: the U.S.
Electrifying solutions
Advances in drilling technology have made it easier than ever to produce petroleum at a time when humanity should use less of it for the planet’s sake.
Until and unless electric vehicles become dominant, it will prove extremely hard to wean the world off of oil.
I believe that governments and automakers should for this reason be working together for the long term. By providing strong incentives for consumers and industries to make the jump, they can stop letting cheap oil stymie climate action.
Otherwise, as hundreds of millions more people become drivers in coming decades, the laws governing supply and demand could steer all of us down a road to devastating degrees of global warming.
Scott L. Montgomery is a lecturer at Jackson School of International Studies, University of Washington.
This article originally appeared in The Conversation. Read the article here.






















