Donations Seek To Save Tunisia From Covid Catastrophe
With Tunisia's health system close to collapse after being overwhelmed by a surge of Covid-19 cases, other countries and even individuals have stepped in to stem the crisis.
European and Gulf nations, Tunisians abroad and ordinary citizens have organised equipment and vaccine donations that are now helping to battle the pandemic.
The small North African nation of 12 million people had been struggling to come up with the necessary vaccine doses even before Covid-19 really began to hit hard.

Now more than three million doses, most of them donated, have been sent, with the number set to reach five million by mid-August, the health ministry says.
China and the United Arab Emirates have each supplied 500,000 doses, while neighbouring Algeria gave 250,000.
Jean-Baptiste Lemoyne at the French ministry for Europe and foreign affairs told AFP that France this week alone sent more than one million AstraZeneca and Janssen doses, enough to vaccinate "a tenth of the adult population".
But either because of sluggish diplomatic efforts by Tunisia or the global shortage of doses, vaccines have arrived late.

Tunisia has received just a sixth of the number of doses promised under the Covax programme, set up to ensure a fairer distribution of Covid-19 vaccines to lower-income countries.
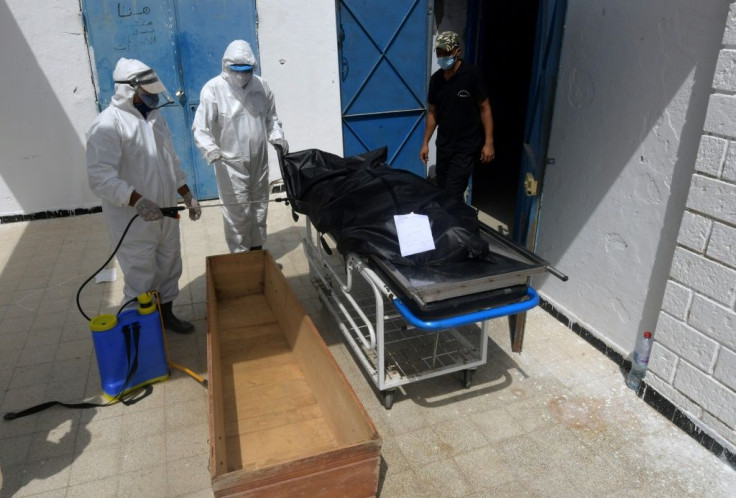
It now has one of the world's highest coronavirus death rates.
According to an AFP count on Wednesday based on official reports, Tunisia recorded 1.4 daily deaths per 100,000 population over the previous seven days, placing it second-worst globally on this metric after Namibia.

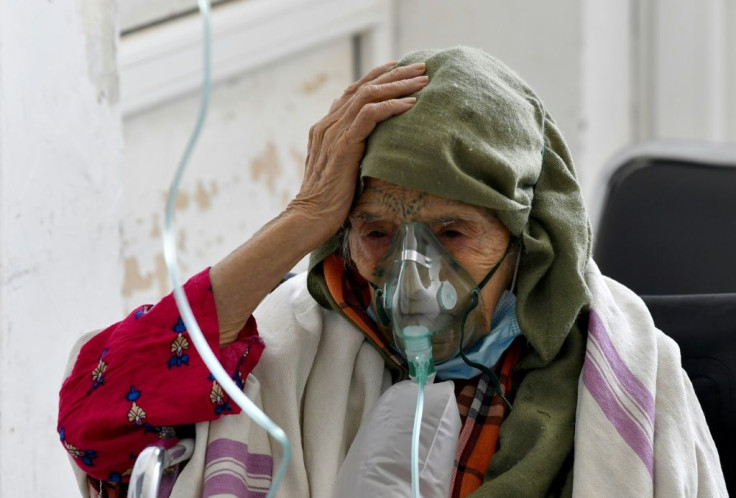
Tunisian internet users have shared videos of panicked families unable to find beds for loved ones, of medics worrying about oxygen shortages and of bodies crammed into swamped morgues.
Dr Hechmi Louzir of the Pasteur Institute in Tunis told AFP that donations will mean the vaccination programme can speed up, and thus reduce the spread of the virus.

Tunisia could "achieve our goal of vaccinating about 50 percent of the population by mid-October", he said.
Even in pre-Covid 'normal' times, Tunisia's public hospitals suffered from poor management and a lack of resources.
At the beginning of summer, they put out a plea for help -- for personal protective equipment and intensive care resources in particular.
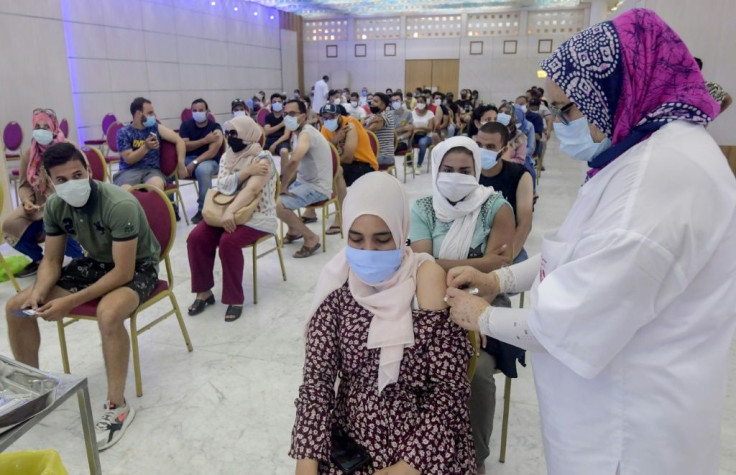
Groups including the country's organisation of young doctors, Tunisian embassies abroad and even private citizens organised fund-raising events.
"The mobilisation of civil society saved Tunisia from a catastrophic scenario," said gynaecologist Cyrine Chedly, a member of an organisation of young doctors in Kairouan.
The central city was one of the first to be badly hit by the pandemic, with some bodies left lying in rooms next to live patients for up to 24 hours because of a lack of staff to take them to overstretched mortuaries.
"Donations of oxygen concentrators have made it possible to reduce the number of serious cases and deaths" at the city's main hospital, Dr Chedly said.
Ons Jabeur, the celebrated Tunisian tennis player now in Tokyo for her third Olympics, auctioned two racquets and raised $27,000 to help finance an intensive care unit.
Before the pandemic, the country had only 90 intensive care unit (ICU) beds in the public sector: now, helped by donations, it has 500.
Tunisians arriving from abroad are allowed to import one oxygen concentrator per traveller, free of import duty.
Doctors post pictures of these items and other equipment on social media, to show donors they are being put to use.
But providing more sophisticated health care equipment can be stymied by coordination problems and bureaucratic obstacles.
One field hospital supplied in May by the United States was not up and running until July, and another donated by Qatar is still not operating because of a lack of oxygen.
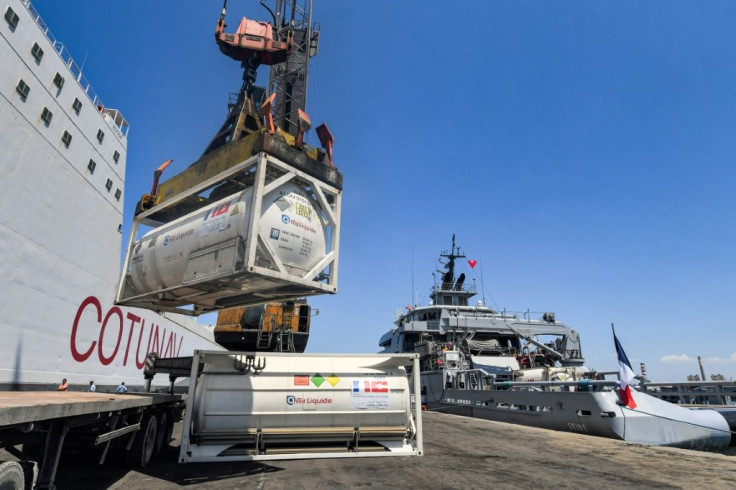
Of three oxygen generators, each capable of feeding 300 beds continuously and supplied by France at the beginning of June, just one is fully functional.
In the meantime, both France and Italy have sent containers loaded with oxygen cylinders to help make up the shortfall.
Arab countries including Algeria, Egypt, Qatar, Saudi Arabia and the UAE have all sent medical equipment.
Mauritania even offered to send 15 tonnes of fish.
Donations alone will not end a crisis spurred by poor observance of preventative measures by the public and by political power plays, which have seen a succession of health ministers in the last year or so.
"We need public awareness, sound management by the authorities of the health crisis and political stability," said Dr Chedly in Kairouan.
© Copyright AFP 2024. All rights reserved.





















