Gonorrhea Symptom: Bleeding In This Body Part After Vaginal Intercourse Could Be A Warning Sign
KEY POINTS
- >555,608 cases of gonorrhea reported in the U.S every year
- Gonorrhea is the second most notifiable disease in the country
- Vaginal bleeding after sex could be a warning sign
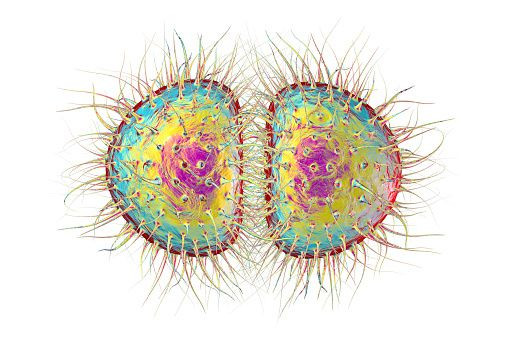
With more than 555,608 cases reported every year, gonorrhea is the second most reported notifiable disease in the U.S. The bacterium Neisseria gonorrhoeae which causes gonorrhea grows and multiplies easily in warm and moist areas of the reproductive tract including the cervix, uterus and fallopian tubes in women and in the urethra among men.
The early warning sign of gonorrhea: Vaginal bleeding after sexual intercourse
Symptoms of gonorrhea infection in women include vaginal bleeding between periods, especially after vaginal intercourse. Women with gonorrhea are at a higher risk of developing serious complications from the infection, whether or not the symptoms are severe. Vaginal bleeding can be accompanied by pain especially during or after having sex.
When the infection spreads, gonorrhea can also cause stomach pain, nausea, vomiting, fever, chills, and sweats. In severe cases, rectal bleeding and pain might also be experienced.
Other symptoms of gonorrhea in women include painful urination, abdominal or pelvic pain and increased vaginal discharge. Symptoms of gonorrhea in men include painful urination, pus-like discharge from the tip of the penis and pain or swelling in either testicle.
This sexually transmitted disease (STD) can also affect other parts of the body including eyes, throat, and joints and cause symptoms such as eye pain, sensitivity to light, pus-like discharge from the eyes, sore throat, swollen lymph nodes in the neck and septic arthritis.
Sexually active women below 25 years of age and men who indulge in same-sex sexual relationships might be at a higher risk of acquiring gonorrhea. Other factors that can increase your risk of getting gonorrhea include having a new sex partner, indulging in sexual relationships with a partner who has other partners, having sex with more than one person and having a history of gonorrhea or other sexually transmitted infections.
When left untreated, gonorrhea can lead to several complications including infertility (in both men and women), birth complications, higher risk of HIV/AIDS and infection that spreads to other body parts.
The best way to prevent STDs like gonorrhea is to practice safe sexual relationships such as using a condom, limiting the number of sex partners, refraining from having sex with someone who has a sexually transmitted infections (STI). You should also get tested for STIs annually.
© Copyright IBTimes 2024. All rights reserved.






















