Somalia At Risk Of Famine 'Catastrophe': UN Agencies
Millions of people in Somalia are at risk of famine, with young children the most vulnerable to the worsening drought, UN agencies said Tuesday, warning that the troubled nation is on the brink of a humanitarian catastrophe.
Many parts of Somalia are being ravaged by an extreme months-long drought that has also taken hold in other countries in the region including Ethiopia and Kenya, destroying crops and livestock and driving huge numbers of people from their homes.
"Somalia is facing famine conditions as a perfect storm of poor rain, skyrocketing food prices and huge funding shortfalls leaves almost 40 percent of Somalis on the brink," the World Food Programme, Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO), humanitarian agency OCHA and the United Nations Children's Fund said in a joint statement.

"We are literally about to start taking food from the hungry to feed the starving," WFP Somalia country director El-Khidir Daloum said in the statement, describing the nation as "on the cusp of a humanitarian catastrophe".
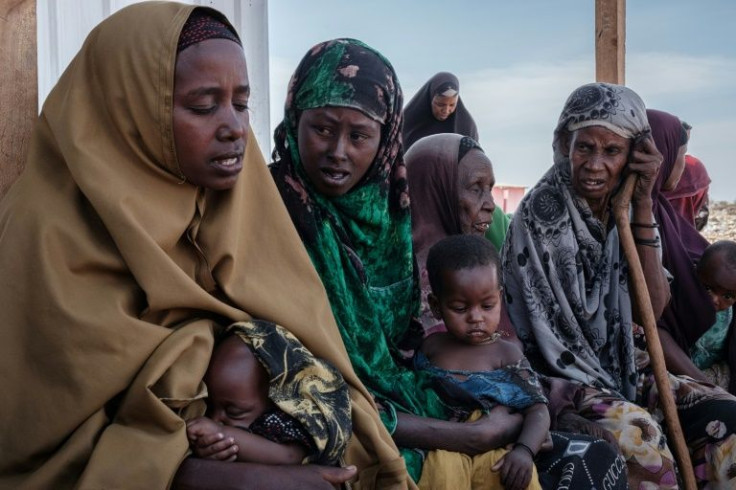
Six million Somalis or 40 percent of the population are now facing extreme levels of food insecurity, according to a new report by the Integrated Food Security Phase Classification, almost a two-fold increase since the beginning of the year, the agencies said.
About 1.4 million children face acute malnutrition through the end of the year, with around one quarter facing severe acute malnutrition, they said.

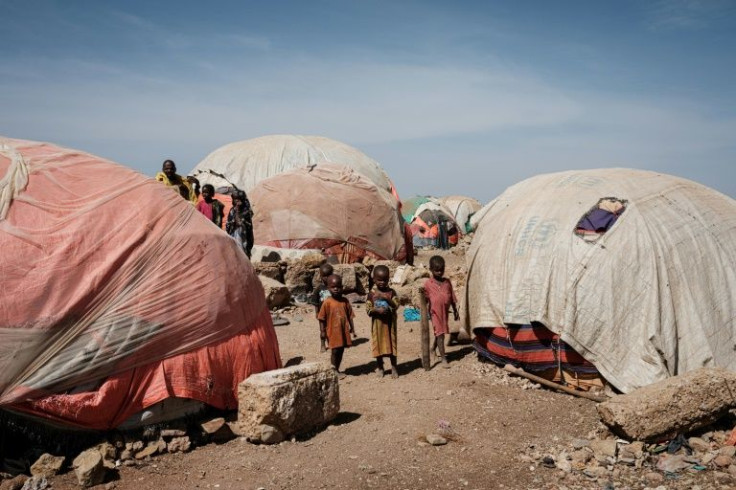
Children under the age of five are the most vulnerable, with access to food and milk scarce because of rising commodity prices and livestock issues.
Six areas have been identified as "at risk of famine, that are at risk of going down that route of 2011 if we don't act now", Lara Fossi, deputy country director for WFP Somalia, told a press conference in Geneva.
She was referring to Somalia's devastating 2011 famine, which saw 260,000 people -- half of them children under the age of six -- die of hunger or hunger-related disorders.
Fossi said there were "huge surges" of people moving across the country in search of humanitarian assistance.
The Norwegian Refugee Agency said 745,000 people had been forced from their homes because of the drought that followed three failed rainy seasons, citing figures from the UN refugee agency.
The UN statement said that together, humanitarian agencies had been able to reach almost two million people but warned of a "critical gap" in donor funding, with a 2022 plan seeking $1.5 billion reaching only 4.4 percent of the target.
Etienne Peterschmitt, the FAO representative in Somalia, said attention had been diverted by the war in Ukraine that has also driven up prices of food and fuel.
The NRC noted that almost all of Somalia's wheat comes from Ukraine or Russia, with prices already spiking for wheat, sugar and oil in parts of the country.
Natural disasters -- not conflict -- have in recent years been the main drivers of displacement in Somalia, a war-torn nation that ranks among the world's most vulnerable to climate change.
The country is also in the grip of a political crisis over long-delayed elections and has been battling an insurgency by the Al-Shabaab Islamist extremist group for more than a decade.
© Copyright AFP 2024. All rights reserved.











