Study: Red Wine, Blueberries, Passion Fruit Aid In Weight Loss
A new study from Purdue University has discovered the presence of piceatannoI in red wine that has the potential to interfere with fat cell development in the human body. PiceatannoI is a compound found in grapes, blueberries and passion fruit with a structural property similar to the much known resveratrol. The study is seen as a forerunner for anti-obesity measures
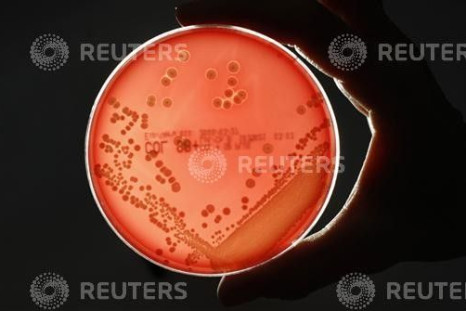
New Study Explores Virus To Fight Superbugs
The Society for General Microbiology's Spring Conference currently being held in Dublin between 26-29 March proposed the use of viruses called bacteriophages to wipe out bacterial strains that are resistant to the current crop of antibiotics. In a proactive stance, the FDA has been warned legally to
to act on its long-drawn 35-year-old ruling that restricts the use of popular antibiotics in farms food.
Genes Define Ageless Skin, Now Nanoparticles Provide Hope
The quest for the ultimate anti-aging skin solution has now found its magic in scientifically developed nanoparticles obtained from shrimps and lobster. The search for the best anti-aging remedy has led a group of scientists to observe gene markers for long- term skin regeneration. At the American Academy of Dermatology's annual meeting in San Diego last Friday, new research on genetic implication on skin and its aging process were discussed .
Yale Study: Cell Phone Use in Pregnancy May Trigger ADHD Syndrome in Offspring
Yale researchers have determined that pregnant women who use their cell phones close to their abdomen might be exposing their unborn child to attention deficit syndrome. The study however states that advanced research is required to determine whether the potential risks of mobile phone exposure during pregnancy had the same impact on humans as it did with the animal models.
Scientists Repair Eyesight Using Human Cornea From Stem Cells
Two separate studies from Spain and Sweden have attempted to cue in on developing epithelial cells that keeps the cornea in its transparent form. While Swedish scientists have grown stem cells on human corneas, their Spanish counterparts have regenerated the corneal epithelium by using cells from the healthy limbus of patients with corneal damage.
Study Supports Single Flu Super Vaccine to Wipe Out Infections
In a new study, researchers observed for the first time that a universal vaccine could allow for a more wide-scale prevention of flu by restraining the ability of the influenza virus to spread and mutate. According to experts, the new study is a first attempt to understand the population consequences of the next generation of vaccines as regards the epidemiology and evolutionary impact on the virus.
Ovarian Stem Cells Holds Promise for Infertile Women: Study
Researchers at the Massachusetts General Hospital have isolated egg producing stem cells from human ovarian tissues. The new study is seen as a precursor to solving fertility issues in women of reproductive ages. If made viable, the study could benefit young women undergoing cancer therapy and older women who have to resort to egg donors.
Teenage Brain More Sensitive to Cocaine: Yale Report
New insights into teenage brain functions have provide a new lead on why adolescents are more addicted to cocaine.
Chess Experts Are Better at Viewing Game Boards, Faces and Other Visual Information: Study
Researchers at the School of Behavioral and Brain Sciences (BBS), University of Texas (UT), have endorsed that a game of chess definitely broadens an individual's outlook in processing visual information.
Study Proves the Last is the Best – Last Chocolate, Last Kiss and Last Interviewee
They say the best is yet to be and now psychologists say the best is the last! Psychologists at the University of Michigan claim to have proved that whether it is a chocolate or sweet or even a kiss, it is the last one which is the best.
Scientists Rate Metabolic Breathalyzer Technique Better Than Blood Tests for Detecting Disease
Scientists at the University of Wisconsin-Madison are in the process of developing a breakthrough breathalyzer technology that would enable early and quick detection of symptoms related to type 2 diabetes mellitus, cancer, obesity, metabolic syndrome and polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS).
Lancet Study: 1.24 Million Malaria Deaths Globally in 2010, Surpasses WHO Estimates
A new study published in the Lancet claims that malaria caused over 1.24 million deaths worldwide in 2010. In comparison to the WHO estimates of 655,000 global deaths as an underlying cause of malaria, the new analysis concluded that global deaths had risen from 995,000 in 1980 and fell to 1.24 million in 2010. The analysis said that death rates were highest at 1.82 million in 2004.
A Silky Heart: Scientists Develop Artificial Heart Tissue From Tropical Silkworm
In a breakthrough effort, scientists at Max Planck Institute for Heart and Lung Research in Bad Nauheim, Germany have build an artificial cardiac tissue using silk from the tropical “tasar” silkworm. According to the researchers, the fiber produced by the tasar silkworm had several advantages over other substances that were tested in the past.
Biochip Detects Glucose in Saliva Instead of Blood for Diabetes Check
A new technique based on biochip detection of glucose in saliva instead of blood is likely to eliminate blood pricks for easy diabetes checks. The specially designed biochip could detect glucose levels similar to the levels found in human saliva.The study explained that the technique takes advantage of a convergence of nanotechnology and surface plasmonics, which explores the interaction of electrons and light (photons).
Study Links Obesity and Pain: Heavier the Individual, the Higher the Level of Pain
Researchers have associated obesity to pain stating that people who are overweight suffer from higher incidences of pain. In the new study, the researchers also indicated that as people age, excess weight is associated with even more pain, as part of the developmental process.
Men More Susceptible To Mild Memory Loss than Women: Mayo Study
New research from the Mayo Clinic Study of Aging has suggested that more than six percent of all Americans between 70 and 89 develop MCI every year. The study noted that men, especially those with high school education, were more likely to be affected.
Iron Protein In Legumes Could Tackle Iron Deficiency Diseases
A new study published by the American Society for Nutrition, reveals an alternative mechanism for the absorption of ferritin - a large, protein-coated iron mineral found in legumes and dried seeds. The study intends to tackle global iron-deficiency illnesses by including more legume-rich diet in the developing world.
Teardrops Could Enable Early Detection of Cancer
University of California (UC) Irvine scientists have established the existence of a disease-fighting protein in human tears that could go a long way in early detection of cancers and other chronic diseases.
Illegal Abortions on the Rise Globally: Study
A new study analyzed links between abortion incidence and the legal status of abortion and stated that 95 percent of abortions in Latin America are unsafe in comparison to 40 percent of those in Asia. The study noted that “restrictive abortion laws are not associated with lower abortion rates.”
Harvard Muffin Makeover Ruins Low Fat Diet Myth
The Culinary Institute of America (CIA) worked on a muffin makeover, with nutrition experts from the Harvard School of Public Health (HSPH), to study healthy breakfast or snack options and the impact of ready- to-eat low-fat diet choices. The study gauged if homemade muffins were a safe bet, compared to donuts and other store-bought muffins, as a healthy snack break.
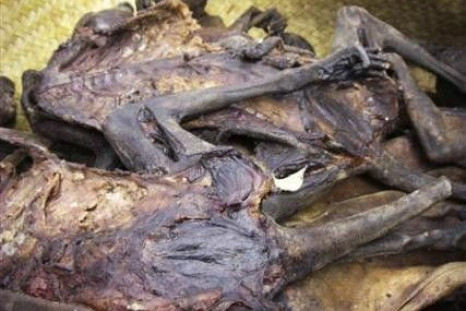
Archaeologists Uncover 3,000-Year Old Tomb in Egypt, with Remains of Female Singer
Egyptian and Swiss archaeologists have uncovered a rare tomb of a female singer, dating back 3,000 years in the Egyptian Valley of the Kings in Karnak, near Luxor in Upper Egypt. The discovery is important because this is the first tomb unearthed from the historic Egyptian valley that has no lineage to the Egyptian Royal family.
Now Decode Your DNA for $1000
The wish to decode your own DNA for as much as $1000 is no longer a pipe-dream. A new bio-technological innovation has made it possible to sequence an individual's genome in a day's time for $1000.
Illegal Wildlife Imports Threaten U.S. Public Health: CDC
A collaborative study led by the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) has identified proof of retroviruses and herpes viruses in illegal wildlife imports at several international airports in the U.S.
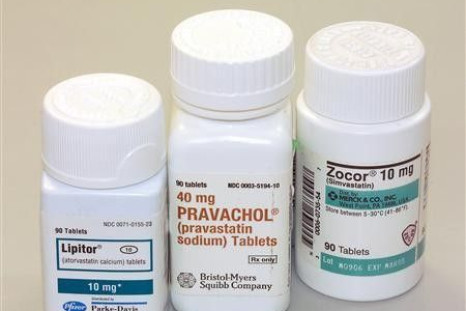
Statins Could Aggravate Diabetes Risk in Women: Study
Diabetes could be an added risk for women taking the cholesterol-lowering drug, more popularly touted as statins.
Study: Nicotine Patches Could Heal Mild Memory Loss
Nicotine patches as a quit-smoking aid have two advantages. The good news is that nicotine patches have now been shown to combat memory loss in elderly people and those who have stopped smoking. According to a study published in the current issue of Neurology, published by the American Academy of Neurology, wearing a nicotine patch could help people with mild cognitive or memory impairment.
Studies Link Vitamin D to Lowered Heart Health and Depression-Related Syndromes
How much Vitamin D can one safely consume? Two unconnected and recently released studies linked the vitamin to an unhealthy heart and depression-related syndromes.
Writing Meaningful Thoughts is Akin to Weight Loss Exercises: Study
It could be that the act of writing down values and beliefs is the next big fat-buster, as part of a mental diet strategy.
Study Relates Fitness as an Indicator for Test Scores at Schools
A new study has linked physical activity to academic performance in children, a finding that could trigger action in the right direction, given the decline in physical activities in most schools.
New Biomarker in Blood Could Detect Extent of Heart Attack: Study
The presence of - troponin I - a biomarker protein in muscle tissue that indicates heart muscle damage, could indicate a person likely to suffer from heart attacks, according to a study published in the Journal of the American Medical Association (JAMA).
Viagra Can be a Wonder Drug Against Heart Failure: Study
Viagra has finally been proven as a savior for heart aches. The new discovery on Viagra’s surprising 'relaxing' effect might actually save lives, according to researchers from the Ruhr Universitat Bochum (RUB), Germany in collaboration with colleagues from the Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minnesota.