The number of Kenyans who will need food aid due to drought will rise to 3.5 million by September, the United Nations said on Tuesday, while European officials warned such crises would flare up again unless more money was directed at prevention efforts.
Yellowstone National Park's landscape may be totally altered by 2075 as climate change increases the frequency pattern of large wildfires, according to a new study released in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
Large fires in Yellowstone National Park could significantly increase due to climate change, drastically altering the park people know today, a new study suggests.
Global warming will cause more wildfires at Yellowstone National Park. The combination of the wildfires and rising temperature will fundamentally change the ecosystem at Yellowstone, possibly by as soon as 2050, according to a new study led by Professor Anthony Westerling of the University of California, Merced.
Shrinking sea ice due to global warming could be the cause forcing Polar bears to swim to distant lands looking for favorable denning areas.
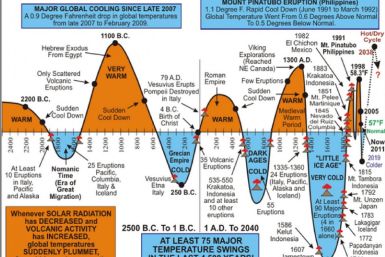
The effects of human-induced global warming were reduced by one third by stratospheric aerosols, according to a study by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA).
Scientists thought it was volcanoes that caused a mass extinction on earth 201 million years ago (this extinction paved the way for the rise of dinosaurs).
Global warming, a detectable trend in the 1980s and 1990s, all but disappeared in the 2000s.
A huge release of methane gas may have triggered the prehistoric mass extinctions that allowed dinosaurs to become the dominant life form on earth, according to a new study.
Richard Marles, the Australian government's Parliamentary Secretary for the Pacific, warned the United Nations Wednesday of rising sea levels and their impact on low-lying islands and asked them to include climate change as a global security issue.
A senior United Nations official warned that climate change could become a catalyst for sudden and abrupt shocks worldwide and have far-reaching implications for global stability and security. Achim Steiner, executive director of the U.N. Environmental Program, told the U.N. Security Council Wednesday that natural resources are at risk.
Poaching of apex consumers has dramatic effects on animals and humans alike
Forget wind power and extra efficient lightbulbs -- trees are an incredibly effective climate change weapon given the amount of greenhouse gases they absorb, according to a new study in the journal Science.
Researchers at the US Geological Survey (USGS) has concluded that last year's seasonal El Nino was responsible for severe erosion along the West Coast during the winter and could be an indicator of things to come.
The extreme heat wave isn't just an American thing.Here is a world tour of heat waves.
Noctilucent Clouds were first observed in 19th century but their appearance has increased over time and are seasonal, appearing most often in late spring and summer every year.
A nuclear power plant in Shimane, Japan, was closed down recently as millions of jellyfish clogged in to the reactor's cooling system.
Four nuclear reactors in Japan, Israel and Scotland were forced to shutdown due to infiltration of enormous swarms of jellyfish, which clogged the seawater cooling system of the plants.
Thanks to a single, female ancestor -- a brown bear from Ireland, who lived around 20,000 to 50,000 years ago - polar bears can now know where they came from, a study in the latest version of Current Biology shows.
Palaeontologists have discovered a near-complete skeleton of the largest marsupial that ever existed.
The Chinese burning of coal may explain why global warming has halted in the last 10 years, according to a study published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS).
Global warming temporarily halted over the past decade instead of apparent increase in greenhouse gas emissions.