A man in New Brunswick, Canada, recorded a video in which fast moving clouds take the shape of a face that resembles Abraham Lincoln.
NASA is preparing to launch a more advanced rover to delve even deeper into the history of Mars, just as its current rover is hitting its stride.
NASA's Mars Exploration Rover (MES) Opportunity after painstakingly covering a 13-mile journey in three years has reached the Red Planet's Endeavor crater.
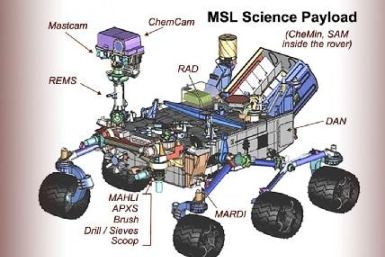
NASA is pushing the boundaries of technology as it readies its next mission to Mars, loading up its fourth Mars Rover with nearly a dozen instruments and employing an innovative but risky landing procedure.
NASA is moving closer to launching its 4th rover on a mission to Mars that will investigate whether Mars is, or whether it has been hospitable to microbial life.
NASA created a deep space mission department to oversee deep space manned mission explorations such as traveling to space rocks and Mars.
NASA has opened a new office called the "Human Exploration and Operations Mission Directorate" to oversee deep space manned missions. NASA was charged by Uncle Sam to put astronauts on an asteriod by 2025, and Mars by mid 2030s.
Mars Rover Opportunity has reached its next destination, the massive Endeavour crater.
As NASA?s Mars Exploration Rover Opportunity landed on its new site, Endeavour crater, on the Martian surface on August 9, scientists assumed it started paving way towards possible future human missions to planet Mars.
After a nearly three year journey, NASA's Mars rover "Opportunity" has reached its destination at a edge of a crater-rim , sending back photographs of never seen before rocks.
NASA reaches its destination, the Endeavour crater, where it will study rocks and terrains never seen by the human eye.
The Mars rover Opportunity is nearing the end of a three year voyage to the Endeavor crater, a massive formation that has been Opportunity's destination since it left the smaller Victoria crater in August of 2008.
NASA's Mars Exploration Rover Opportunity will revisit the rim of Endeavour crater on Mars, where its rover twin Spirit finished its mission in May.
Start the slideshow to view images from NASA?s past Mars expeditions suggesting evidence of water on the Martian surface.
Scientists have discovered flowing salt water on Mars, which has sparked conversations about potential alien life within the planet's surface. The images sent from NASA's orbiter unveiled flowing waters descending down from rocky slopes.
The mysterious dark lines in question were observed to be occurring seasonally as the ground they came from was exposed to warmer temperatures. The line would then disappear later as temperatures dropped, causing the scientists to speculate that briny water was causing the flows. The discovery could be a huge breakthrough in the search for whether or not liquid water ever existed on the surface of Mars.
New evidence suggesting the existence of water flowing on Mars indicates the possibility for life to exist on the Red Planet.
NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter revealed on Thursday that highly salty water may flow on Red Planet during the warmest months, which raise the chances that life could exist on Mars.
Scientists found evidence of saltwater on Mars. Shifting dark streaks on the planet's surface imply that there is water flowing on Mars.
Scientists have found new evidence of possible salt water flows on Mars, which could lead to traces of life being found on the red planet.
NASA scientists said on Thursday that new evidence indicates that highly salty water may flow on Mars during its summer, which also empowers the possibility of life on the planet. The reason behind the thought that life could be possible in Mars is that compared to ice, liquid water is more likely to sustain life, a fact that stresses the significance of the latest discovery.
NASA scientists have discovered new evidence that briny water flows on Mars during its warmest months, raising chances that life could exist on the Red Planet, the space agency said on Thursday.