Win The Vote But Still Lose? Behold The US Electoral College
"Beautiful" is how US political outsider Donald Trump described his shock presidential win against rival Hillary Clinton on the night of November 8, 2016.
The details were less clean-cut.
Former secretary of state Clinton had received nearly three million more votes than her Republican rival.
But, by narrowly winning key battleground states, Trump surpassed the 270 Electoral College votes necessary to win the White House.
With just five weeks until the 2020 election featuring Trump and Democrat Joe Biden, the rules of this enigmatic -- some argue outmoded -- system are coming back into focus.

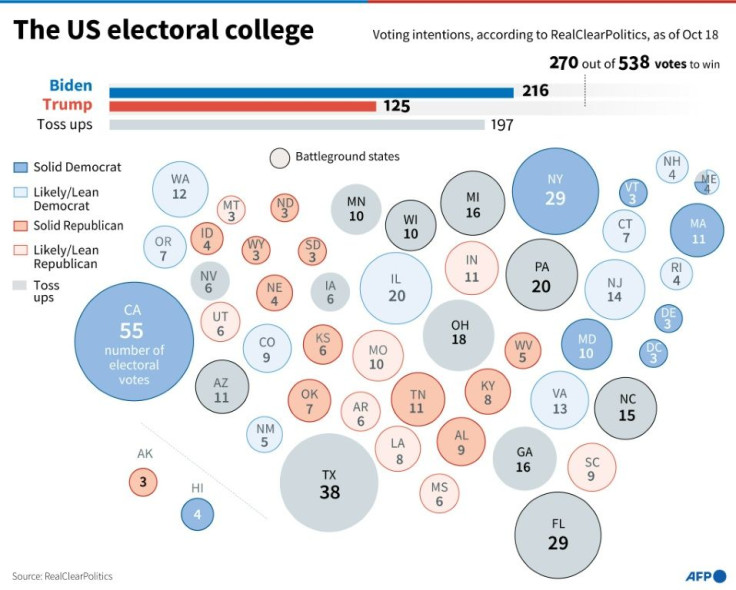
The 538 members of the US Electoral College gather in their state's respective capitals every four years after the presidential election to designate the winner.
A presidential candidate must obtain an absolute majority of the college vote -- or 270 of the 538 -- to win.
The system originated with the US Constitution in 1787, establishing the rules for indirect, single-round presidential elections.
The country's Founding Fathers saw the system as a compromise between direct presidential elections with universal suffrage, and an election by members of Congress -- an approach rejected as insufficiently democratic.
Since then, hundreds of amendments have been proposed to Congress in efforts to modify or abolish the Electoral College, but none has succeeded.
Debate was rekindled with Trump's victory. If 2020's race is a nail-biter, then the Electoral College will surely return to the spotlight.
Most are local elected officials or party leaders, but their names do not appear on ballots, and their identities are mostly unknown to voters.
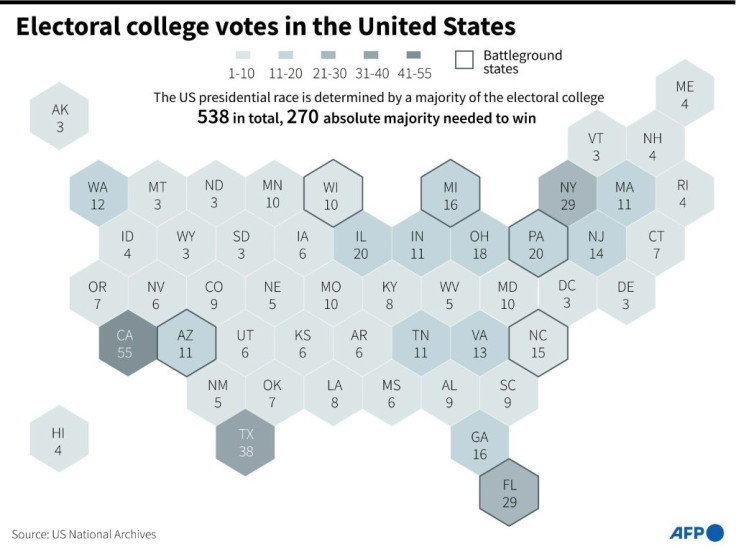
Each state has as many electors as it has members in the House of Representatives (a number dependent on the state's population) and in the Senate (two in every state, regardless of size).
California, for example, has 55 electors; Texas has 38; and sparsely populated Alaska, Delaware, Vermont and Wyoming have only three each.
The Constitution leaves it to states to decide how their electors' votes should be cast. In every state but two (Nebraska and Maine), the candidate winning the majority of popular votes theoretically wins all that state's electors.
In November 2016, Trump won 306 electoral votes. Indignant, millions of Americans had signed a petition calling on Republican electors to block him. The effort was mostly in vain, as only two electors, in Texas, defected, ultimately giving him 304 votes.
Republicans had denounced the move as a desperate attempt by activists refusing to accept defeat.
The extraordinary 2016 situation of losing the popular vote but winning the election was not unprecedented. Five presidents in all have risen to the office this way.
John Quincy Adams was the first, in 1824, against Andrew Jackson. More recently, the 2000 election resulted in an epic Florida entanglement between George W. Bush and Democrat Al Gore.
Gore had ultimately won nearly 500,000 more votes nationwide, but when Florida was awarded to Bush, it pushed the Republican's Electoral College total to 271 -- and victory.
Nothing in the Constitution obliges electors to vote in one way or another. If some states require them to respect the popular vote, and they do not, such so-called "faithless electors" were subjected to a simple fine.
But in July 2020, the US Supreme Court ruled that states could impose punishments on such disloyal voters by establishing laws mandating electors to cast their votes according to the popular vote in that state.
Between 1796 and 2016, some 180 electors cast votes contrary to the presidential or vice presidential candidate who won their state. But faithless electors have never determined a US election outcome.
Electors will gather in their states on December 14 and cast votes for president and vice president.
Why this date? US law states they "meet and cast their vote on the first Monday after the second Wednesday in December."
On January 6, 2021, Congress will certify the winner, who gets sworn in on January 20.
© Copyright AFP 2024. All rights reserved.





















