69-Year-Old Masturbates In Front Of Relatives After Suffering Stroke
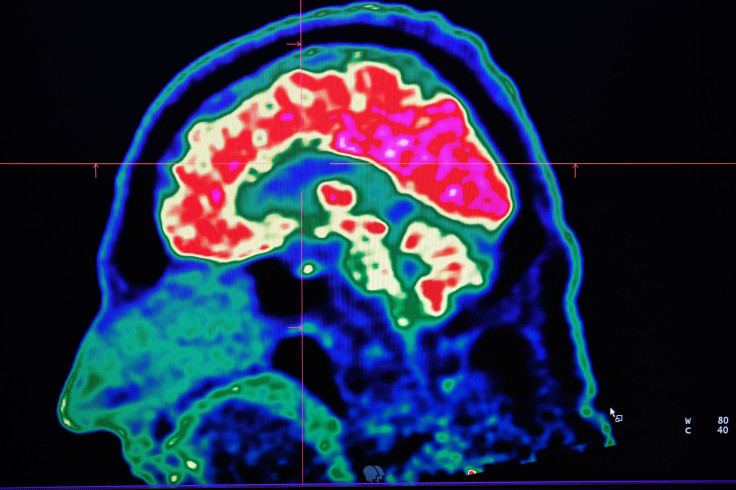
A 67-year-old man masturbated in front of his relatives after a stroke caused him to think there was nothing wrong with public exposure. The incident took place in Spain.
According to the Daily Mail, the man's family was concerned after they started noticing drastic changes in his behavior. The bank manager, who has not been identified, was taken to a hospital in Mostoles, 16 miles southwest of Madrid.
The family members also told doctors that the man had addressed them with inappropriate sexual words, and they were worried about the sudden change in his character.
Doctors at Hospital Universitario de Mostoles reportedly conducted several tests on the unnamed man and found no abnormalities with his brain function. To find answers, medics decided to arrange a CT scan, which showed what they feared - it resembled a "non-aggressive brain tumor."
Dr. Rafael García Carretero's team concluded that the man suffered from subacute anterior cerebral artery stroke, which was "silent" and occurred with little to no symptoms.
The unnamed man was hospitalized for a week and his neurological symptoms improved, the medics revealed in the BMJ Case Reports. He was treated with aspirin and atorvastatin drugs that reduce the risk of another stroke.
"His relatives said he once again became nice, judicious, prudent, thoughtful and well-mannered," the team of doctors wrote in the journal.
Dr. García Carretero added: "The man was never aware of his changes and his family said he had problems interpreting others' moods."
In the medical journal, the team continued: "Frontal behavioral syndromes caused by strokes are rarely reported."
According to a health website, effects of a Frontal Lobe Stroke include muscle weakness, speech and language problems, a decline in thinking skills and behavior and personality changes.
In behavioral changes, patients sometimes may feel excessive jealousy or lack of empathy. Other common behavioral changes after a frontal lobe stroke include profound lack of initiative and motivation, spontaneous expression of rude or odd remarks, irritability, carelessness and apathy, inappropriate and seemingly random persistence and repetition of certain behaviors.
© Copyright IBTimes 2024. All rights reserved.




















