7.7-magnitude Earthquake Generates Small South Pacific Tsunami
A 7.7-magnitude earthquake struck in the South Pacific on Thursday, generating a small tsunami that caused no damage to island nations in the region before authorities gave the all clear.
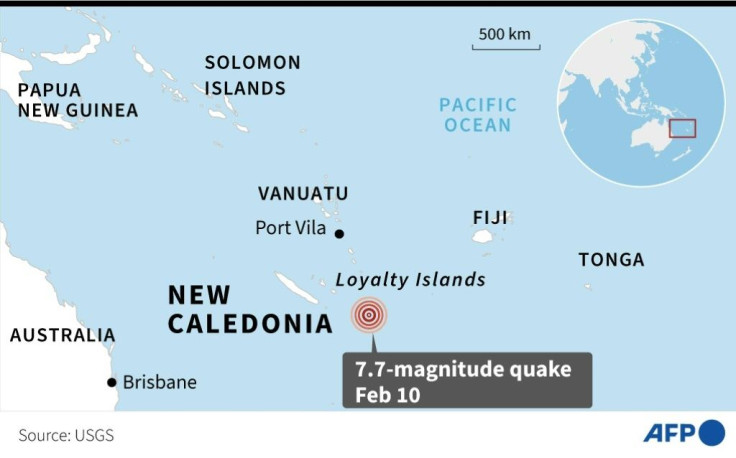
The quake struck at just after midnight on Thursday local time (1320 GMT Wednesday) about 415 kilometres (258 miles) east of Vao in New Caledonia at a depth of 10 kilometres, according to the US Geological Survey.
The US government's NWS Pacific Tsunami Warning Center said "hazardous tsunami waves" were forecast for some coasts.
It said waves reaching between 0.3 and one metre above the tide level were possible for Fiji, New Zealand and Vanuatu.
A wave of 0.3 metres struck Fiji, according to the Twitter feed of the island nation's seismology department.
However, Fiji Seismology later cancelled its tsunami warning.
"The seismology observatory upon its assessments has now verified and confirmed the cancellation of the warning and 'all clear information' (is) issued to the whole Fiji group," it said.
The Australian Bureau of Meteorology confirmed in a tweet that a tsunami had been generated.
The bureau warned of a threat to Lord Howe Island, which is about 550 kilometres (340 miles) east of Australia's mainland, but said there was no need for evacuations.
Locals in the Vanuatu capital Port Vila said they felt the quake but there was no damage from either the shake or subsequent waves.
The New Zealand National Emergency Management Agency warned of "strong and unusual currents" in northern coastal areas but said there was no tsunami risk.
"There isn't a threat to land so we haven't issued a tsunami alert," the disaster agency's acting director Roger Ball told Radio New Zealand.
He advised those in affected areas to "stay out of the water and stay off the beaches" but said the danger posed was not enough to warrant a nationwide warning.
"Waking everybody up at 4:00 or 5:00 am in the morning with emergency mobile alerts we didn't feel was a proportionate response," he said.
There were no initial reports of casualties or damage from the tsunami or the quake, which was initially recorded by USGS at magnitude 7.5 before being revised to 7.7.
The Pacific "Ring of Fire", where tectonic plates collide, experiences frequent seismic and volcanic activity.
In 2018, a 7.5-magnitude quake and subsequent tsunami on Indonesia's Sulawesi island left more than 4,300 people dead or missing.
A 9.1-magnitude quake struck off the coast of Indonesia's Sumatra island in 2004, triggering a tsunami that killed 220,000 throughout the region.
The death toll included around 170,000 in Indonesia -- one of the deadliest natural disasters in recorded history.
© Copyright AFP 2024. All rights reserved.




















