US Fed Expected To Sit Tight As Trump Tariff Fears Buffet Markets

The US Federal Reserve is widely expected to extend its rate cut pause on Wednesday as it seeks to chart a path through the economic turbulence unleashed by President Donald Trump's on-again, off- again approach to tariffs.
Since taking office in January, the Trump administration has ramped up levies on top trading partners including Canada, China, and Mexico -- only to roll some of them back -- and threatened to impose reciprocal tariffs on other countries, spooking US financial markets, which have slumped in recent weeks.
Many analysts fear Trump's tariffs, civil service job cuts, and immigration plans could push up inflation and hamper economic growth, and complicate the Fed's plans to bring inflation down to its long-term target of two percent while maintaining a healthy labor market.
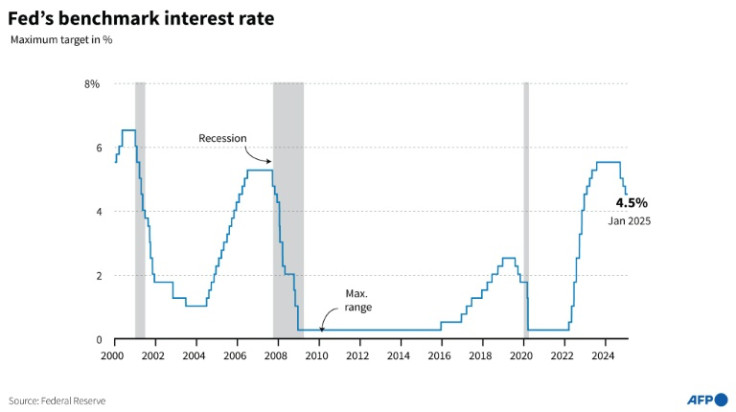
As inflation remains too high, Fed policymakers are likely to hold rates steady at between 4.25 and 4.50 percent, and to signal they will wait for more clarity on the economic impact of the new administration's policies before contemplating a cut.
"There'll be no change in the interest rate, and there's a good reason for that," former Boston Fed President Eric Rosengren told AFP.
"It's quite unclear how high the tariffs will get, how widespread they will be, and how long they will last," he said. "And it's very hard to estimate what the impact on inflation or unemployment is going to be until they get a little more visibility into that."
Policymakers on the Fed's rate-setting committee will also publish updated economic forecasts on Wednesday, with many analysts anticipating trade uncertainty could cause them to increase their inflation outlook slightly, and to downgrade their predictions for economic growth.
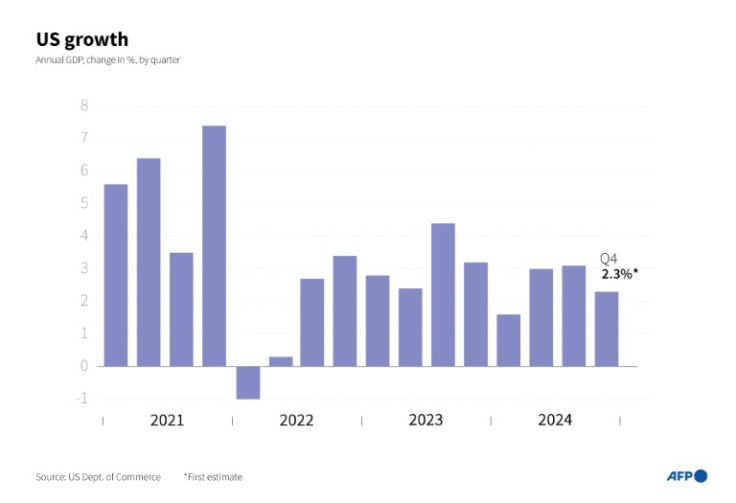
Until recently, the hard economic data had pointed to a fairly robust American economy, with the Fed's favored inflation measure showing a 2.5 percent rise in the year to January -- above target but down sharply from a four-decade high in 2022.
Economic growth was relatively robust through the end of 2024, while the labor market has remained fairly strong, with healthy levels of job creation, and an unemployment rate hovering close to historic lows.
But the mood has shifted in the weeks since Trump returned to the White House, with inflation expectations rising, and financial markets tumbling, since the stop-start rollout of tariffs.
"We do not need to be in a hurry, and we are well positioned to wait for greater clarity," Fed Chairman Jerome Powell said at an event this month, alluding to the uncertainty about the effect of Trump's economic plans.
While Fed officials have sought to avoid criticizing the new administration, some analysts have been less restrained.
"US President Donald Trump's management of economic policy has been a disaster," Michael Strain, the director of economic policy studies at the conservative American Enterprise Institute, wrote in a recent blog post.
"Previously, it would have been unfathomable for a president -- including Trump during his first term -- to inflict so much harm on the economy deliberately," he said.
In its December economic outlook, Fed policymakers penciled in two quarter-point rate cuts for this year.
Amid the trade uncertainty, economists at Barclays wrote in a recent note that they expect policymakers to dial that back to just one cut this year.
"Fed officials want to be careful not to overreact," Nationwide chief economist Kathy Bostjancic told AFP, adding she expects the Fed to pencil in two cuts this year in its forecasts, but to ultimately make just one.
"There's so much uncertainty," she said, adding that she hoped to have more clarity on the US economy after the planned rollout of Trump's retaliatory tariffs on April 2.
© Copyright AFP 2024. All rights reserved.





















